Chapter 12 Download Chapter
How Effective?
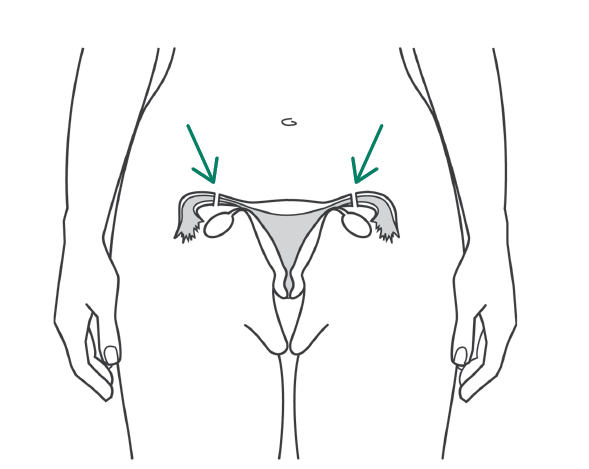
One of the most effective methods but carries a small risk of failure:![]()
- Less than 1 pregnancy per 100 women over the first year after having the sterilization procedure (5 per 1,000). This means that 995 of every 1,000 women relying on female sterilization will not become pregnant.
- A small risk of pregnancy remains beyond the first year after the procedure and until the woman reaches menopause.
- Over 10 years of use: About 2 pregnancies per 100 women (18 to 19 per 1,000 women).
- Effectiveness varies slightly depending on how the tubes are blocked, but pregnancy rates are low with all techniques. One of the most effective techniques is cutting and tying the cut ends of the fallopian tubes after childbirth (postpartum female sterilization).
Fertility does not return because sterilization generally cannot be reversed. The procedure is intended to be permanent. Reversal surgery is difficult, expensive, and not available in most areas. When performed, reversal surgery often does not lead to pregnancy (see Question 7).
Protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs): None.